DFS: AN ECOSYSTEM FOR THE NEXT PHASE OF FINTECH TRANSFORMATION
By Rezaul Hossain | August 9, 2020

More than 5 Billion people and business, and at least 20 billion devices by 2020 will be connected through digital technology. With people, businesses and devices communicating, transacting and trading with each other, a new world comes into being- the digital business sphere, where digital financial service will play a vital role.
Evolution of Money: A Brief Introduction
Digital Financial Service promises rapid development of new capabilities that will give competitive advantage. One of those advantages will be integration of many low and middle income individual and SME into financial inclusion domain. Digitization of transaction, purchase, business and financial products is expected to expedite financial inclusion.
In developing countries, most people and small business are not fully integrated into the formal financial system. They rely on cash for all their transaction, do not have feasible tool for investing and cannot access formal lending options. DFS can address this problem with one unique digital account (wallet) which will remove the current entry barrier, by facilitating transaction, payment, loan/financing as well as provide access to e-commerce and thus improve the quality of lives of millions of people.
Some upcoming phenomena
• Flexible registration process through electronic subscription (e-KYC)
• Device becomes part of lifestyle (convergence of voice, data, finance)
• Wider Merchant eco-system with both physical & e-selling
• New type of payment/ Convergent payment mechanism acceptable at all platform (virtual token)
• Digital bank will enter and way of working of traditional banking will be changed
• Emergence of block chain technology
Rise of MFS/ MAFS
Over the years, Mobile Financial Services (MFS)/Multiple Access Financial Services (MAFS) has evolved from a simple money transaction channel to comprehensive financial solution platform and the journey has been fueled by both growing business needs and progress in technology.
Since 2005 several initiatives been taken by different entities to launch MFS, but failed. Key reasons of failure were:
1. Tried to implement merchant payment only
2. Not using certain structure to acquire customers to open account
3. Services limited to few utility payment, top-up etc.
4. No option for cash in or cash out
5. Lack of efficient cash management system
Safaricom Kenya in 2017 launched M-PESA money transaction service through mobile USSD which was a Telco-led model with a support of Kenya government. It immediately became popular and dramatically increased people’s access to financial service, though its S&D structure was not full proof.
M-PESA drove customers use of mobile phones to send and receive money, pay merchant and utility bills, as an alternative to the traditional banking system. One of the key reasons of M-PESA’s success was cultural, that many Kenyans used to work in metro areas leaving their families in villages. M-PESA campaign “Send money home” got huge response among those working class people, which constitutes a major chunk of the population.
With its sister service, M-Shwari, users now able to save money and take loans, all without the much dreaded waiting hours, charges, vetting and paperwork like traditional banks. Due to M-PESA’s success, financial inclusion among Kenyans grew from 27% in 2006 to 75% in 2016. This becomes a successful model for mobile money throughout the world. M-PESA becomes part of the life of Kenyan people that now as a nation Kenyans are proud of three things: Runner, Big five and M-Pesa.
Today there are 30 million users in 10 countries and a range of services including international transfers, loans, and health provision. The system processed around 6 billion transactions in 2016.
In the same time some other players launched payment and money transfer through other access channels such as mobile apps, QR code etc. Paytm in India is a good example on that. Paytm is a Reserve Bank of India (RBI)-approved e-wallet. Users can simply pay by either scanning a QR code of the shop or by entering the mobile number of the recipient. As of end of 2018, 280 million people are now using Paytm to pay for their daily utilities and other expenses. Paytm invested an amount of 500 Crore Indian rupees to promote the brand through the campaign “Paytm Karo”.
India government’s decision of demonetization worked as a catalyst for the popularity of Paytm. Demonetization forced people to switch to either plastic money or a digital payment method. This helped Paytm to further consolidate their position in the domain of e-payment application.
One of interesting point as per the licensing guideline of the Reserve Bank of India, cash in or cash out is not allowed from Paytm or any such digital money service.
Chinese players: WeChat and Ali pay introduced more advanced feature such as chat pay. Money transfer through messaging apps as well as in-app purchase from ecommerce/marketplace is such a thing which has opened up another window for the digital revolution.
WeChat, an initiative of Tencent holding, started its journey in 2010 as a messaging app. Since then, it has grown into the most popular mobile app in the country with over 1 billion monthly active users who chat, play games, shop, read news, pay for meals and post their thoughts and pictures. Through its multiple innovative services this app has converted Tencent Holdings, into one of the most influential companies in China and grabbing the attention of global investors.
To understand the WeChat universe, it is important to take a look at its underlying product philosophy. It’s all about one word – ‘connect’. WeChat wants to connect to everything, it wants to plug into the user’s life, whenever and wherever possible.
Alipay is a part of Ant Financial’s ecosystem of financial services, a initiative of the Chinese e-commerce giant Alibaba Group. In 2004, Alibaba Group launched Alipay to support online payment on Alibaba.com and Taobao.com. Alipay quickly become the leading online payments service provider in China, claiming more than 50% market share and 47M users by 2007, according to Alibaba Group.
Alipay not only allows mobile based financial transaction and payment but also has expanded its scope into credit scoring, wealth management, insurance, and lending.
With its associated companies, Alipay has 600 million users, which has made it’s the largest fintech player globally.
To drive financial inclusion, Bangladesh bank issued a draft guideline in 2011 and permitted 28 Banks to offer Mobile Financial in bank led model. 18 banks have already launched mobile financial services up to June, 2017. But Except bKash, none of the entities are yet to become successful.
Even Dutch-Bangla Bank Limited (DBBL) which made significant effort following the Bangladesh Bank guideline; couldn’t achieve significant business volume, because the guideline was not right, initially.
Among different services, send money, cash in and cash out constitutes the major chunk of the pie. Through an unique business model, robust distribution network, efficient cash management and aggressive customer acquisition drive, bKash became the “World’s largest mobile financial service provider” in terms of number of subscribers and number of agents within 5 years of launch. bKash also had unique company structure which worked as an accelerator for growth.
Following table illustrates a brief journey regarding rise of bKash as the no.1 mobile financial service provider in the world in terms of subscriber
Following were the key reasons behind success of WeChat and Alipay:
• Low credit card penetration
• Weaknesses of China’s banking system and state-owned enterprises
• China’s transition to a consumption-driven economy
• Need of remote payment for e-commerce
• Innovative product offering: messaging, transaction, insurance, credit in a single ID
Current context: Global
A. As per world bank study in 2017:
2 billion out of the world’s 7 billion do not have access to financial services. 1/3 of the global population 1 billion are in Asia.
Why people unbanked?
• Entry barrier due to unavailability of bank branch / Delivery channel
• Expensive for the customers
• Travel distance from the nearest service delivery point
• Higher cost for bank to serve a customer. Any customer enters in a bank branch costs BDT 128 per visit
• Financial literacy is less
Current context: Bangladesh
Bangladesh has already achieved 37% financial inclusion by 2018 compared to 16% in 2011. Low cost, easy accessibility and convenience of MFS has vastly contributed to the financial inclusion of the country’s “unbanked population” – reaching places & people far better than banks.
• MFS in Bangladesh at a glance:
– 18 active MFS operator
– 67.5 million registered subscriber
– 37.3 million active subscriber
– 3,820 million USD total transaction/month
– 210 Million number of transaction/month
A. Access to DFS:
B. Ownership/access over a mobile handset is the 1st step for getting access in the digital financial services. The device might be a simple bar phone, feature phone or smart phone.
C. Based on the handset ownership we can divide the DFS users into the following 3 major user types:
D. Customer with multiple sim
E. Customer without device (have sim but can’t afford device)
F. Customer with sim & device but not using for transaction (OTC Customer)
G. Customer have nothing
H. As per the BTRC data, there are 156 million mobile subscribers, whereas there total number of handset is 121 million. So, this is clear that: there are 35.5 million pocket sim (Sim without device).
I. Again there is Multiple sim phenomena, hence unique number of mobile subscribers is 92 million in the country
Typical lifecycle of customer
1. Majority of the users at 1st purchase a bar phone or a feature phone, at price range: BDT 650- 2,000, based on his/her financial condition. Major usage is voice call, SMS and few VAS, few multimedia content etc.
2. After using the device from 12 months- 24 months, they switch to entry level smart phone of range: BDT 3,000- 5,000- mostly local brand and Chinese brands. Users started internet and VAS contents, multimedia contents etc.
3. After using the entry level smartphone for around 1 year, certain number of customers switch to Chinese international brands and other global brands, depending on his/her financial condition
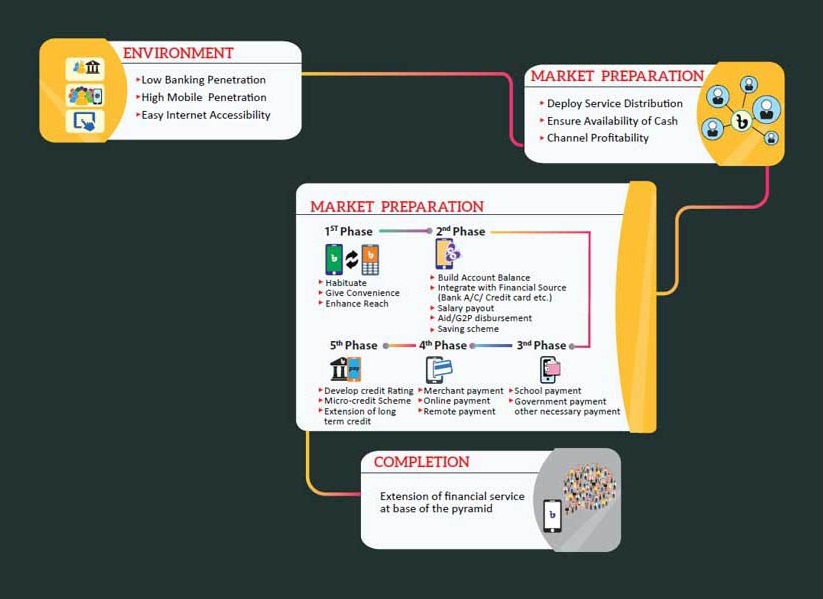
Key elements for DFS eco-system
• Digital Wallet:
For accessing MFS/MAFS financial service, digital wallet is pre-requisite. A digital wallet refers to an unique identity that allows an individual to make electronic transactions, payment etc. End user /enterprise can sign up very easily through e-KYC. After signing up, the end user/enterprise can access the wallet through multiple Access channels (Mobile USSD, Web, Apps, NFC). One single wallet can be used to fulfill all the financial needs of individuals and SME, because digital wallet can be integrated with existing bank account(s), credit card account, loan account etc. All types of payment or collection can be made digitally through this wallet. Therefore, based on this A/C transaction and other business information from ERP, credit rating can be generated and loan can be offered. Their client small business house will use ERP system for their daily business starting from accounting to human resource planning and management, CRM etc. That data will help institutes to analyze and verify credit worthiness. Automatic rating system will help to disburse loan/ financing facility. In this way, digital wallet will play a significant role in digital transformation of the financial institutions/ MFIs
Other players for successful MAFS Rollout
• Regulatory:
The regulatory framework can play a vital role by facilitating the MAFS players in terms of customer acquisition through easy A/C signup process. Efficient cash management is a must for successful MAFS/MFS rollout; the regulator can support this by allowing multi bank fund management facility. Regulator can promote account integration for better mobilization of fund between traditional bank accounts and MAFS/MFS accounts.
For business sustainability of the players, proper Tax & VAT structure is required from the regulatory body.
I. Infrastructure:
For providing easy and convenient access to mass people, significant telecom penetration is a pre-requisite. Justified revenue sharing with access channel partners (MNO) is required to maintain healthy business. Proper data coverage through MNO/ wireless broadband service providers is required to increase adoption of advanced access channel like: Apps, QR code etc.
Nationwide banking coverage is required to support distributors in proper market service. Law & Order Situation of the country impacts the market service and overall business viability.
• Bank:
Availability of adequate cash in bank branches is required along with vault limit and extra hour support to distributors.
• Technology:
Flexible & Scalable system is required to facilitate millions of people to do transaction, payment and other things within a shortest lead time. A user friendly interface is required to convince people for utilizing the MFS/MAFS for their daily financial needs.
Where are we and where do we have to go
• Products and services offered by MFS/MAFS:
• Money deposit (Cash in)
• Money withdrawal (Cash out)
• Send money (P2P)
• Merchant payment
• Government to Person Payments/Person to Government Payments
• Disbursement and collection
• Inward remittances.
• Utility bill payment
• Other payments like microfinance, overdrawn facility, insurance premium, DPS, etc.
• E-commerce payment
• Key changes driven by MFS/MAFS:
MFS has facilitated million of masses with easy access to formal financial system, which is not feasible for traditional banking channel. MFS has helped in faster disbursement of donor agencies fund and also helped in establishing transparency in government disbursement.
Due to increased popularity and wide acceptance of the MFS, conventional banks are losing retail business. Formalization of fund due to financial inclusion is resulting higher revenue for government which actually contributing in GDP growth of the country.
It will be tough for the traditional banks to survive in future, as they are dependent on Interest income & Service charge as the primary source of income.
Ultimate destination is to develop the full fledged DFS eco-system which will comprise all the necessary elements:
• Consumer
• Enterprises/Merchant
• DFS platform and distribution network and access channels to facilitate transaction and payment
• Business Solution (ERP)
• Credit rating and financing, Collection and disbursement
• Selling through market place- local and international
• Nationwide delivery infrastructure
Specifically in a country like Bangladesh implementation of DFS would offer the following key benefits for individual and SMEs:
• Easy access to formal financial system by sign up e-KYC
• Loan facility based on credit rating
• Enhance efficiency through usage of Information Technology/ Business solutions
• Greater access to local and international market through e-commerce, export/import etc.
Products/ Services
MFS/ MAFS: bKash, Nagad
ERP: Kiu
Loan: Kiu/ Ferratum
Market place: Kiu, Daraj (Ali baba)
Delivery: Pathao, Uber
Ultimately, the Digital Financial System (DFS) is about the creation of new business eco-system by bridging the physical and digital elements of business through integration of things; connected with people and business. DFS is driving all the elements of business (customer, enterprise/ merchant, technology, transaction, payment ERP solution, credit rating, financing, e-commerce) towards convergence. Increased penetration of devices and enhanced data connectivity are facilitating consumers with digital wallets, which provides a way to pay, send money, and manage other required transactions.
New streams of granular, real-time data are emerging, and enterprises can use that data to support business decision-making. Alternative funding platforms & Marketplace lenders (like Kiu, Ferratum) are widening access to financing activities and providing fund to a greater number of small and medium enterprises through DFS platform.
This article was originally published at FINTECH